Web Development with Firefox

Rapid Web Development and Testing with Mozilla Firefox
Web Development with Mozilla Firefox
Successful web development requires certain essential tools. One of the
best tools available for web development and testing is the Mozilla
Firefox web browser. 
"Out of the box" Firefox has an extensive list of built in development tools. Secondly, the extensible design of Firefox has encouraged the development of many very useful extensions to help in the design and troubleshooting of web pages. The additional functionality can be a real time saver during the Web development process.
Quick Tip
Another important feature of Firefox is it's standards-compliant rendering engine. Firefox's page rendering has proven to be very close to the official W3C behavior and display recommendations. Consequently, web pages that render correctly in Firefox usually work reasonably, if not perfectly, in most other browsers with only minor adjustments.
Built-In Firefox Web Development Tools
Firefox comes with several standard tools that are built into the browser. By themselves, these tools are powerful enough to consider Firefox an essential web development tool.
These tools include:
- An expanded page source viewer.
- The ability to display detailed information about a web page.
- A JavaScript debugging tool.
- A real-time DOM inspector and editor.
Viewing the Source of a Page
Like most browsers, Firefox provides the ability to view the source of a page. Firefox offers a different twist, though. Instead of sending the source code to an external text editor, Firefox uses its own source viewer with syntax highlighting and color coding of the html tags.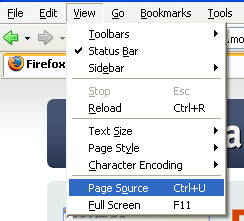
When content on a web page is highlighted, Firefox also offers the option to view the selected source by opening a version of the source code view, with the selection's markup highlighted in the source. This makes it easier to find a specific section of a web page in the overall source code.
Quick Tip
You can view the source of a page by choosing "View > Page Source" through the menu system or by choosing View Page Source form the context menu (keyboard shortcut Ctrl-U).
You can view only part of the source of a page by highlighting a portion of the web page and then right-clicking to bring up the context menu and choosing "View Selection Source".
Page Info Reports
Firefox provides detailed information about a page through the Page Info window.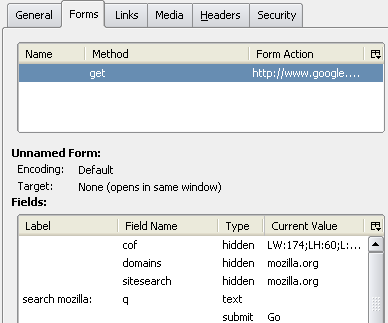
- The General tab displays information about the page such as url, size, and rendering mode.
- The Form tab displays the forms on the page and details about the fields in the forms.
- The Links tab lists the links in the page, including hyperlinks and style sheets.
- The Media tab contains information about all media on the page, such as images and favicons.
Quick Tip
You can access the Page Info window from "Tools > Page Info" or by right-clicking on the page and selecting "View Page Info" from the context menu.
Javascript Console
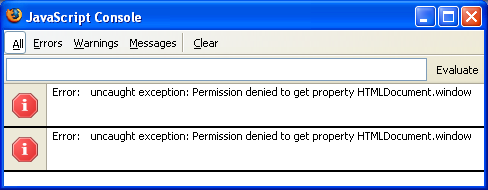
The Javascript Console is a tool for JavaScript developers to write and test javascript code snippets or external JS files. The console provides an interface to use XPCOM components, a means for dynamic script loading, and the reporting of Javascript related and CSS errors in the web page.
DOM Inspector
The DOM Inspector provides direct access to the Document Object Model. For each element, the inspector provides a list of information including which CSS rules are affecting any given element in order of their cascade priority. For quick access to the DOM for a selected element, you can also install the Inspect Element extension. 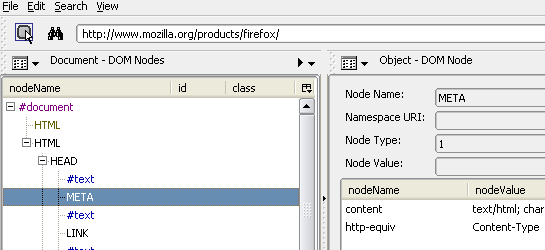
Quick Tip
Firefox comes with the DOM inspector, but on Windows machines, you need to choose it when you first install the browser. To do this choose "Custom Install" and then select "Web Developer Tools". Once installed, the Firefox DOM Inspector is under the Tools menu.
Firefox Web Development Extensions
In addition to the built in developer tools, Firefox provides the ability to add additional web development functionality through the use of add-on programs called extensions. Some of the most useful extensions are described in the following slides. Many more developer extensions are available on the Mozilla update site. Look under the developer tools submenu to find additional web developer extensions.
The Web Developer Extension
This extension, by itself, makes Firefox an indispensable tool for Web development and testing.
The Web Developer Extension adds a toolbar to the browser containing various web developer tools. It outlines page elements, displays the size of images, gives CSS and form information, disables certain elements on a page, and much more.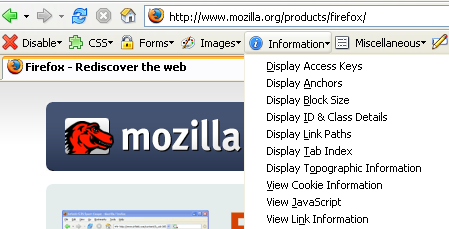
Accessibility
Accessibility
Extensions for Firefox helps in the testing of a page's structural markup
to meet the needs of people with disabilities. Fangs gives a textual representation of a page, similar to the way it is read by a screen reader. For more accessibility testing try the Accessibar Firefox extension or the Web Developer Extension.
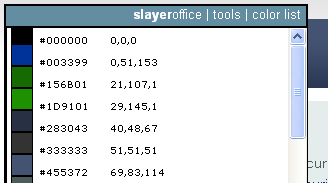
Colors
Colorzilla is
an eyedropper tool. Hovering over an element
shows color info, DOM path info, and the X,Y offset from the previous click.

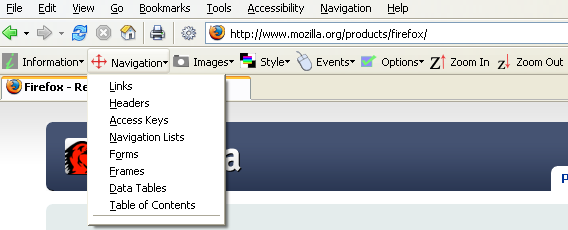
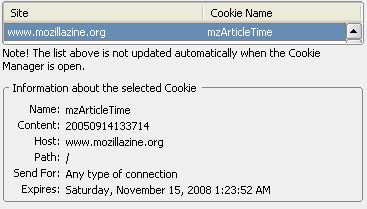
Cookies
The Add & Edit Cookies extension allows for the adding and editing on cookies to a page. This extension is a more featured version of the View Cookies extension.
CSS
The CSSViewer inspects elements on a page to give a complete rundown of the CSS declaration for a chosen element.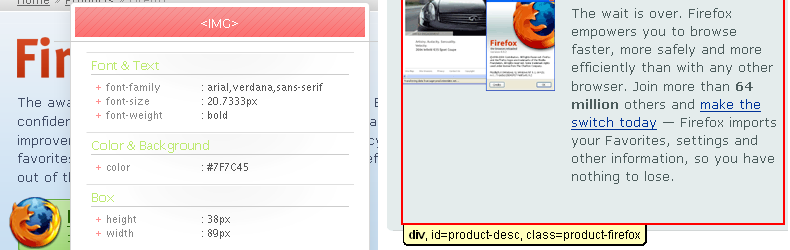
Aardvark is a CSS debugger with
keyboard modifiers. It displays items on the page such as the element name and id or class
name of a selected element.
Quick Tip
For the Aardvark extension, as you glide the mouse over the page, you will see a red rectangle framing each element under the cursor. You will also see a little yellow caption showing the HTML element type and its class or id if they exist.
Debugging
Firebug helps in debugging AJAX, DHTML, and JavaScript web applications. It will display errors that occur during the rendering of a page, will place the pointer on the appropriate line, and allows for the inspection of different values of the DOM.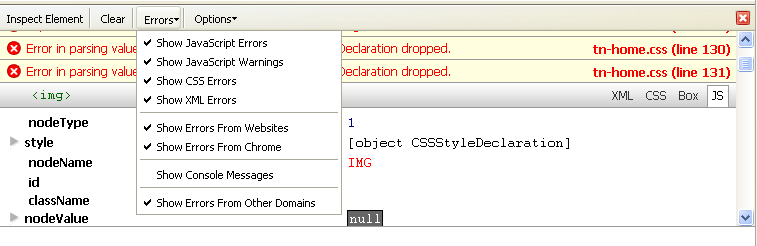
Links
LinkChecker
checks every link on a web page to find bad links. The simple color
coding scheme makes it easy to quickly spot a bad link on a page.

Measurements
MeasureIt draws
a ruler across a web page to display the width, height, or alignment of any
page element.

Page Information
The Extended Statusbar extension adds information to the status bar displaying the average download speed, bytes downloaded, load time, number of loaded images and percentage of the page loaded. It is similar to Opera's status bar.

The MetaTags Sidebar extension displays information from the source code, such as the code lying between the
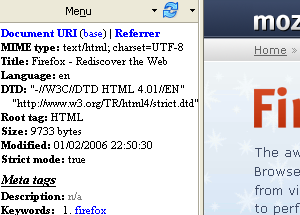
Page Parameters
Live HTTP Headers displays information about the HTTP headers on a page in real time.
UrlParams is a sidebar extension that displays the form parameters Firefox has sent to the server on the last request. It will also let you change or add parameters and re-submit the request.
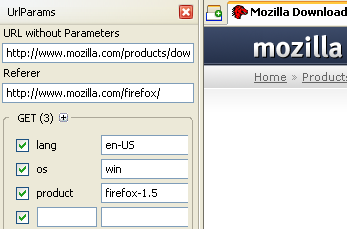
User Agents
User Agent
Switcher allows Firefox to identify itself as a different web browser,
such as IE or Opera, to a web server.
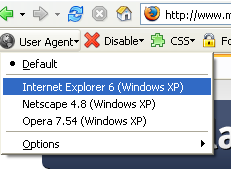
View Pages in Other Browsers
IE Tab is an extension that launchers your URL in Internet Explorer inside of a Firefox tab. A simple time saver when checking pages for cross-browser compatibility.
IE View allows the current page or a selected
link to be opened in the Internet Explorer browser. OperaView provides the same functionality for the Opera web browser. In addition, FirefoxView allows you to open Firefox to the current page or selected link from within Internet Explorer.

Firefox Bookmarklets
Bookmarklets (favlets) are small JavaScript programs that are stored as
a URL within a browser's bookmark and add additional functionality to the
browser. While most of what bookmarklets can due are already bundled into
extensions, two good sources of bookmarklets can be found at Slayer
Office and Square
Free. The Slayer Office Favlet Suite is particularly useful to show things
such as a list of colors on a page or to change hidden fields on a form.
Firefox Developer Tools Extensions
In addition to extensions which help a developer to code and test a page there a several Firefox extensions that are designed to complement/replace various desktop development tools. These extensions provide an interesting alternative to software such as Filezilla or Nvu.
Editors
Codetch is a code editor for various markup languages. It emulates many of the features seen in Dreamweaver into a editor inside of Firefox.
Screenshots
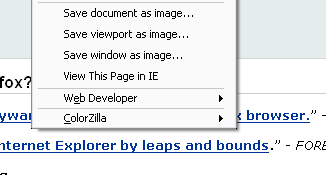
The Pearl Crescent Page Saver saves an image of a web page to a file in PNG format. The Page Saver extension uses the new canvas feature that was introduced in Firefox 1.5.
The Screen Grab extension takes a screenshot of a web page in several different ways. Most importantly, it allows you to capture the entire web document that you are viewing.
The End
While it may seem daunting at first take the time to get to know many of the extensions mentioned in the previous slides. It will save a lot of frustration and time. Especially become familiar with the Web Developer extension, the CSSViewer extension, and the Firebug Extension. You will be glad you did!